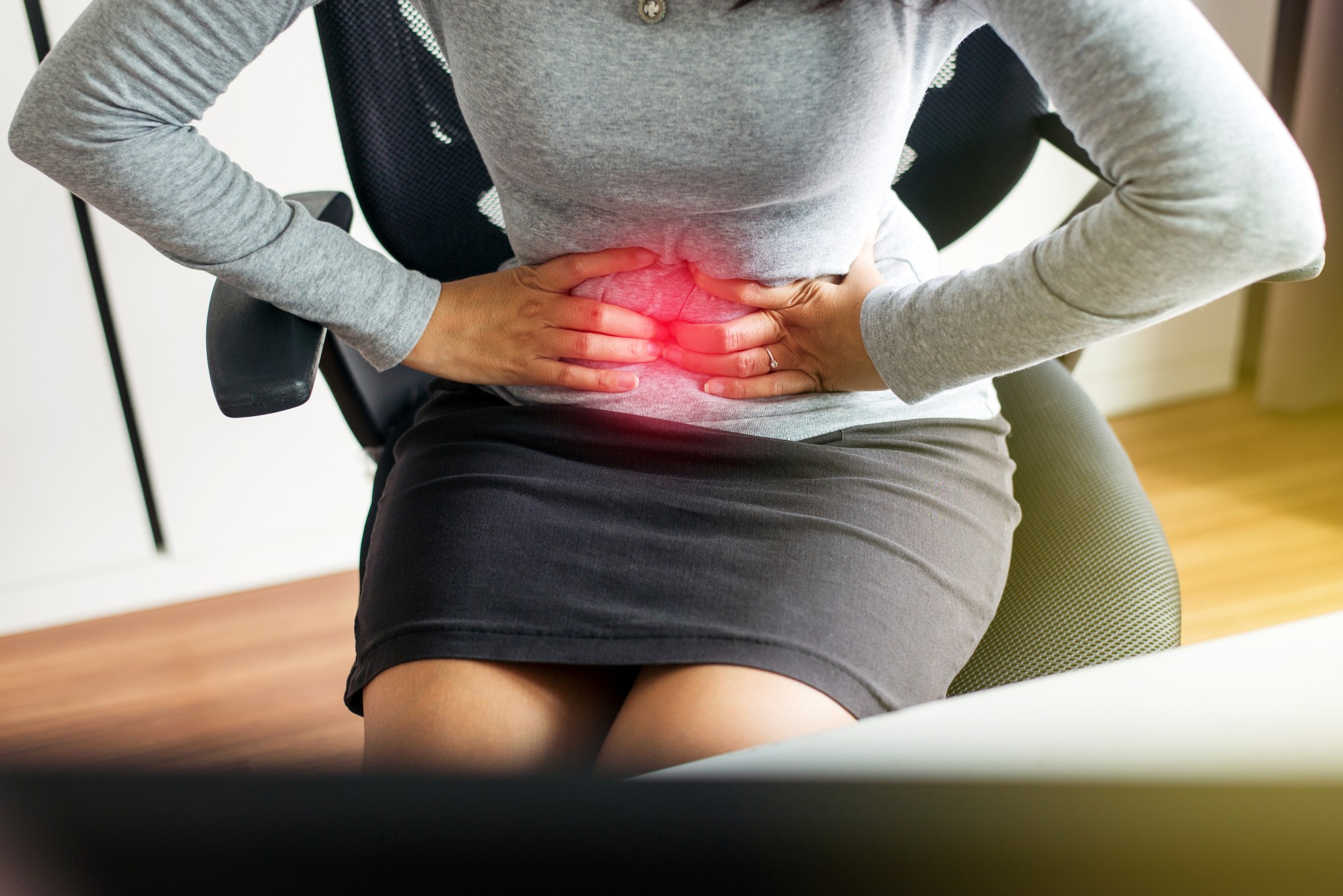
Stomach aches, gas, and heartburn can cause us distress, but the discomfort is typically fleeting. However, sometimes these symptoms may indicate a more serious health condition. There are many digestive disorders ranging from mild to severe and with many possible causes. We’ve identified the top 10 here.
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Those who suffer from frequent acid reflux or heartburn may have Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, commonly known as GERD. Usually, the esophagus pushes swallowed food down through a ring of muscles that connect the stomach and esophagus. Stomach acid can leak back up into the esophagus when these muscles are weakened.
In addition to the burning, the acid can cause severe damage over time. GERD afflicts approximately 20% of Americans and can be treated with lifestyle changes – such as alterations in diet and frequency of meals.
2. Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) and Gastritis: An ulcer is an open sore, and in this case, it appears in the lining of the stomach or small intestine. Gastritis, in contrast, is inflammation of the stomach lining. The two health conditions have similar symptoms, including stomach pain and nausea. They also have common origins – typically a bacterial infection known as H. pylori. Frequent use of aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen may also cause these health issues.
3. Gluten Sensitivity and Celiac Disease: Gluten sensitivity and celiac disease show similar manifestations, including diarrhea, bloating, and abdominal pain. While gluten sensitivity is relatively common, celiac disease affects less than 1% of the United States population. Because they look so similar, it is essential to get an official diagnosis as celiac disease is a severe autoimmune disease. Reducing or eliminating gluten from the diet is the primary treatment for both medical conditions.
4. Stomach Flu: Stomach flu is a viral stomach infection that may also affect the upper part of the small intestine. The most common symptoms of the flu – also known as gastroenteritis – are diarrhea, vomiting, stomach pain, and cramps. While gastroenteritis often clears up without intervention, the patient may lose a significant amount of fluids through diarrhea and vomiting.
Therefore drinking water and electrolyte drinks are necessary to prevent dehydration.
5. Constipation: Constipation causes infrequent or difficult stool passage, typically defined if bowel movements occur less than three times a week. Chronic constipation afflicts approximately 63 million Americans annually. The most accepted cause of constipation is too little fiber in the diet, and increasing fiber, fluids, and exercise will resolve the situation in most cases.
Although laxatives are a standard treatment, most physicians caution using them only temporarily and sparingly.
6. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic digestive tract inflammation, most often identified as Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These are autoimmune diseases that cause irritation and swelling, diarrhea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, fever, and weight loss. The two conditions affect different parts of the digestive system – Crohn’s disease mainly occurs at the end of the small bowel and the beginning of the colon, while colitis affects the colon and rectum.
7. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is abdominal pain, identified by frequent flareups – at least three times a month for three months. Constipation or diarrhea may accompany the pain. Much more common than IBD, IBS doesn’t damage the digestive tract. Although 15 million people in the United States suffer from IBS, the cause of IBS is not known. Most people take laxatives, fiber supplements, or probiotics to treat IBS.
8. Diverticular Disease: Diverticular disease (diverticulosis) results in small pouches on the colon wall that become inflamed. Approximately half of the people over the age of 60 have this condition which makes them feel bloated or constipated. It may also cause pain in the lower abdomen. Bleeding from the rectum is a sign of severe progression, and the patient should see a doctor immediately.
9. Gallstones: The gallbladder stores a digestive juice called bile. In some conditions, bile can form small, hard deposits called gallstones. Some gallstones are not problematic and resolve on their own; however, some can cause severe pain, infection, nausea, vomiting, and fever.
Digestive problems can cause extreme discomfort and disruption to daily life. Although some require medical intervention, many can be resolved through holistic methods.
If you are experiencing symptoms and looking for relief naturally, call the practitioners at Longevity Wellness Clinic for an initial consultation.